A tone curve is a curve that defines a tonal correction operation applied to each pixel of the source image (or, more precisely, to each of its RGB channels). In Filter Forge, this operation is used in the Tone Curve component and the Profile inputs of all noise components such as Perlin Noise component or Stones. Technically, the tone curve defines the output level of a pixel's channel as a function of its original channel level:
OutputLevel = F(InputLevel),
where F is a function defined by the tone curve, InputLevel is the channel level of a pixel in question before the operation, and OutputLevel is the level of the same channel of the same pixel after the operation.
Examples of Tone Curves
Example 1. A linear tone curve doesn't have any effect on the image, because the output channel levels it produces are the same as the input levels:

Example 2. Shifting a linear tone curve upwards produces a brightness increase. The output brightness level is increased by the amount of the upward shift:

Example 3. Rotating a linear tone curve around its middle point increases the contrast of the resulting image:
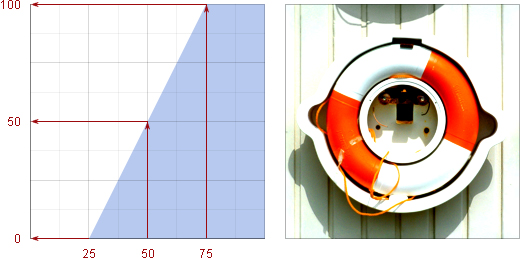
Example 4. A Gamma curve applied as a tone curve performs gamma correction:
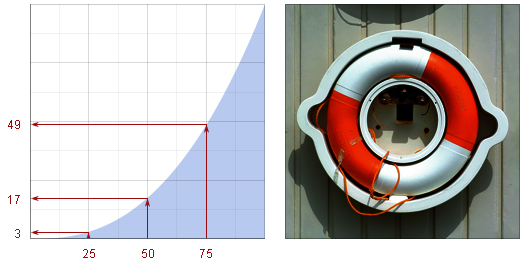
Example 5. A reverse linear tone curve inverts the image: input channel levels are converted to their opposites (0 to 100, 25 to 75, 75 to 25, 100 to 0):
